Abstract
Stablecoins, which are primarily intended to function as a global reserve of value are insubstantial in their design and present many failure points. The primary mechanism to enable the coins to hold on-to a fixed value is by backing them with collateral. Fiat collateralized stablecoins require users to trust a centralized entity, which breaks the total concept of decentralization. Crypto collateralized stablecoins have issues involving high collateral requirements and introduces risks of auto-liquidation. This Research Project aims to propose the use of an alternative architecture for the creation of a functional and secure stablecoin.
1. Introduction
Stablecoins are crypto tokens designed to eliminate volatility by backing it with an asset or fiat currency that remains stable. Further simplifying on the context - A stablecoin is just a token on the blockchain which maintains its value in accordance to a fiat government backed currency. Due to their property of non-volatility, which has been a pre-dominant problem in cryptocurrencies that exist today, it has garnered a lot of interest and appreciation.
However, Stablecoin designs which exist currently are insubstantial and present many failure points, which limits their general acceptability. Fiat collateralized stablecoins require users to trust a central entity, which breaks the total concept of decentralization. Non-collateralized stablecoins implementing seigniorage shares approach are still new and people actually trusting on them is questionable. Slightly better off the Crypto-Collateralized stablecoins, though providing a decentralized ecosystem are not that efficient in maintaining the stability and moreover has issues revolving high collateral requirements and liquidation risk in market crashes. Crypto-backed stablecoins like Dai, from Maker has achieved the feat of decentralization in the system [1], but has instability in their design principles –
• ~1.5 x collateral required
• Collateral can be auto liquidated
Summing up, all-together there is a dire need and opportunity to improve this piece of technology for global reach and acceptance.
2. State of Existing Problems
A. Artificial Markets
The market is dependent on supply-demand relationships. As most of the underlying cryptocurrencies are based on supply-demand relationships, proof of work provides the intended way to mine and produce new coins in the market. The difficulty of the system is adjusted and the target is set in every iteration to generate new coins. The target and reward re-adjustments provide an optimum way to attain stability. Artificial market calls for a solution which could hide the market problems by separating the concerns in token-economics [2].
B. Market Manipulation
Market manipulation allows for any entity to attempt to try and manipulate the market to alter the price of the stablecoins. Furthermore, the existential risk of market collapse also destroys the whole concept of a decentralized cryptocurrency. Controlling or influencing markets can be a cause to destroying the functionality of the whole ecosystem. Manipulating the markets will result in an improper game to play and will take the market down instantly. Summing up the weakness can be divide into two kinds of risk–
1. Risk of market collapse,
2. Oracle/governance manipulation.
3. An Update to the Architecture
The existing problems redirect to a new form of backing the architecture of stablecoins and one way of attaining all the benefits while solving all the problems is by creating collateral backing from third party investments. Broadly speaking, crypto-collateralized stablecoin where the collateral backing is from third party investments would allow a 1:1 collateralization ratio, and while also allowing to use the investor’s funds as a security if/when the price of Ethereum goes down. The stability and the operation of the system is taken care of by the competitive investment process.
A. The process
Users deposit ethers and get an equivalent amount of stablecoins for the collateral provided. Unlike Maker and other crypto backed stablecoins, no extra amount of ether has to be provided by the person. After the stablecoins are exchanged for the collateral amount, the coins and amount need to be secured by someone/ a group of people (crowdfunding) for volatility in the underlying crypto (Ethereum). The volatility is taken care of by the investment circle running in the background. The group of people who secured the stablecoin are entitled for the profit or loss (if any) in the underlying crypto and helps keep the stablecoins stable.
B. Incentives for Investment
The algorithm provides better returns to the investors for providing a portion of the collateral, than just holding on to their Ethereum (ETH)[3] The investment made by people is returned when the original stablecoins are redeemed. The amount returned to each of the investors is not linear to the fraction they provided the collateral for, but exponential for the part of the collateral they provided.
C. External Collateral provision from the Pool
Providing the collateral for the stablecoin through a method of external funding backed by incentives offer for a structure which has two independent parts which function together to make the system functional. The external collateral pool being a separate entity for controlling the stability ensures that the instability of the market is not a concern for the proper functioning of the application. Separating the collateral pool and disconnecting all the relation with the other aspect of the stablecoin structure also allows the system to adapt to an alternate method of gathering collateral if required. This increases on the security aspect and makes sure that the system has a 100% uptime.
4. Explaining competition
A. Anonymity to enforce competition
The portion filled by other agents are anonymous. This provides with a competitive glance to filling up the maximal portion of the collateral amount. After all the agents are done filling up the collateral, an internal threshold is formed which partitions the point of profit/loss on either side.
B. Risk/Reward Gains
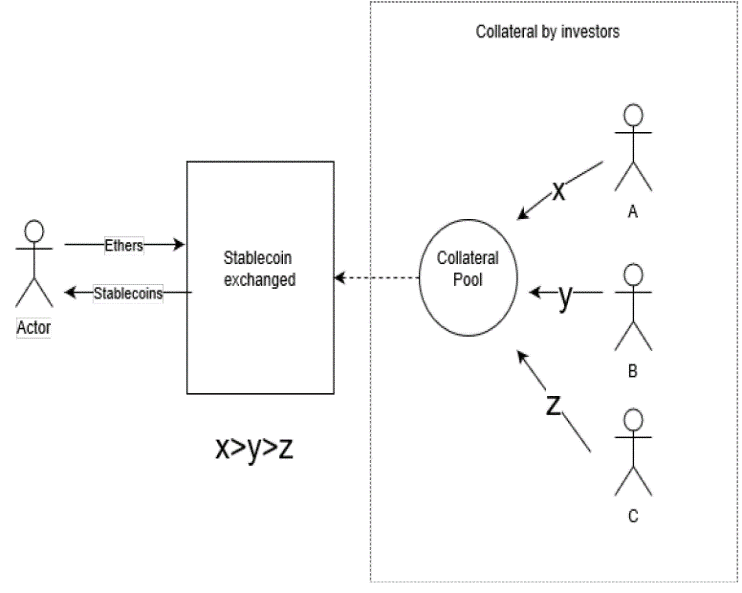
Fig 1: Collateral Pool structure
The Anonymity brings in a concept of a strategic game built into the system. The lenders or collateral providers are provided to maximize their lending capacity considering the risk factor to it. The Rewards are directly related to the amount of investments, and not knowing what the other person has pooled in, makes sense to try and provide the maximal amount for pooling. Only the risk factor is the criteria for slashing the funds if a volatility issue comes up.
C. Keeping the system alive
The competition among the lenders ensures a faster disbursal rate and almost provides with an instantaneous rate for providing with the capital. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins currently in existence provide with a method to collateralize instantly, but this mechanism comes closer while solving a larger scale of problem. The speed of disbursal increases with the competition which is further increased by trust in the system.
5. Explaining the Money-Money Algorithm
A. Designing the algorithm
The Algorithm takes care of the return distribution to the investors to the collateral pool. A strong and intelligent mechanism would motivate the investors and borrowers (the token buyers) to play a strategic game together and keep the system functional. The algorithm tends to provide returns in an exponential form with respect to the amount invested or the rate of involvement in the system.
B. Description of the design
The Algorithm shows the Distribution of the MARGIN (CURRENT ETH VALUE (-) STABLECOIN PURCHASED) in an Exponential way proportional to the Amount invested
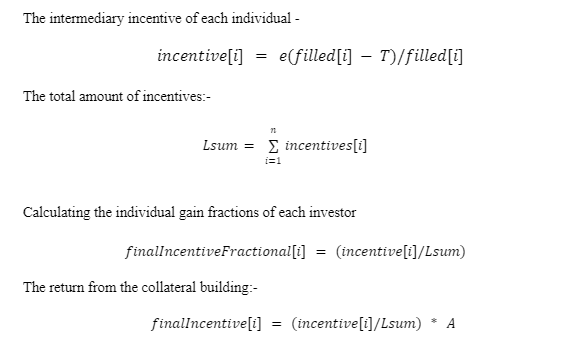
Let,
Incentive[i] = Incentive of individual investor
Lsum = Total amount of collected incentives
filled[i] = Portion filled by ith person
T = Total Limit
A = Amount cumulated
C. Optimal Strategy
The optimal strategy is to fill the highest fraction of the collateral amount to get huge profits in any. The competition among the investors for landing in the better side of the curve (filling the most parts of the collateral), will mean faster fulfillment. To further elaborate the exact advantages of the investors, listing out the two cases-
• When ETH prices go up, people above the optimal point receive a higher profit than what they could have got by simply holding the ETH
• When ETH prices go down, loss is very less compared to what they would have incurred by simply holding the ETH, if they are above the optimal point.
So, irrespective of the direction Ethereum (or the underlying asset) takes, the investor is in a favorable position in all conditions. There isn’t an associated luck factor, since it is clearly evident how a user can settle above the optimal point.
6. Statistics
The stablecoins structure proposed is non-linear type when it comes to the returns offered against investments. Because of the exponential structure of the profits there exists a threshold which has to be crossed in order to attain the profits. The profits are the reason which forces the lenders to push for the extra mile and go for the extra rewards. The competition for the extra reward motivates everyone to compete and increase the disbursal rate.
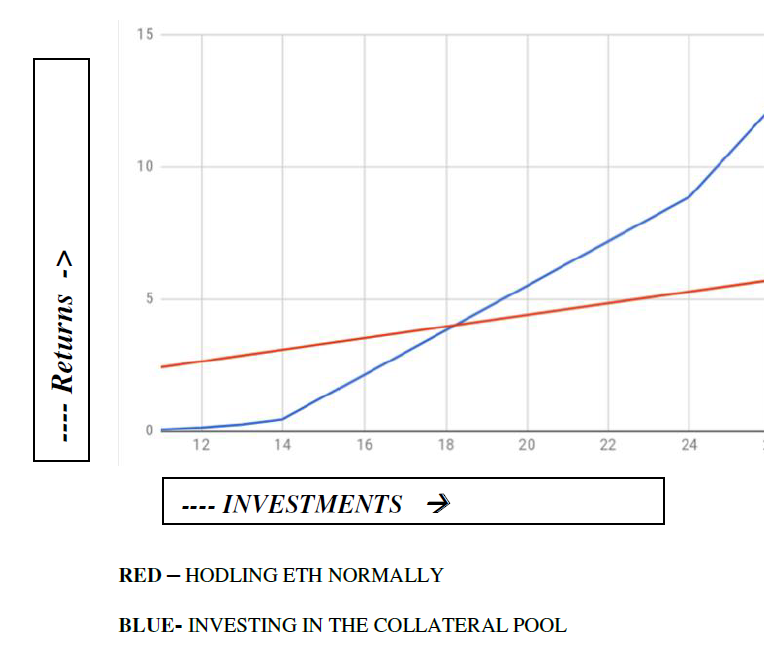
Fig 2: Comparing Incentives vs Investments
The red graph plots the investments to the rewards for a cryptocurrency like Dai, while the blue graph plots the performance of the proposed platform, the point in the center specifies the central point or the threshold to land with extra rewards. Whether it’s a bull or bear crypto market, investing in the collateral pool will mean greater profits or lesser losses for investors, and strengthen a stablecoin architecture on the other side.
7. Additional Integrations
A. Introduction of a Secondary token
A secondary token could be introduced to the ecosystem which could bind both the tokens together when maintaining stability. The secondary token could also be traded in a similar manner with the differences only being in the usage-
• Adjust the supply and demand manually by investors to maintain the stability of the primary currency
• Be used as a token to prevent or distribute losses in a better way in the situation of a high risk volatility
B. Adding a lending service to integrate with the ecosystem
The stablecoin can be considered to be a loan itself, and stablecoins are provided in exchange for a collateral. The ecosystem already uses a method to provide collateral by third-party or entities who are not acquiring the stablecoins. The point of the collateral can be improvised to incorporate a lending structure [4] to make up for the losses by the market volatility. The amount existent in the collateral pool is a possible way to use the money to make up for losses in the system, or can be partnered with a microfinance entity. This also however, could bring up some issues, namely-
• Introduce a separate entity of trust with the collateral pool
• Provide a point of liquidity risk when collateral pool is depleted lower enough than the market capacity [5]
8. Implementation Discussion
Listing out the main components of the ecosystem:-
• Ethereum Smart Contracts
• ERC-20 token
• Wallet
• Interest distribution Algorithm
The stablecoin is designed to be functional at the Ethereum main network as an ERC-20 token standard. The token was created using solidity smart contracts and deployed on the Ethereum network. A secondary token can be created to maintain or further improve the stability of the existing token. The secondary token is the backing token and could also be an investment medium for several third parties. The smart contracts are the way to implement these tokens on the Ethereum framework. Smart contract is a piece of code that lives on the world-computer- the Ethereum Blockchain and maintains the state of the universe. The process of using the token i.e. buying and transferring can be done by interacting with the contract. Instead of the direct interaction with the contract, some users could also prefer to use a wallet service to avoid directly using the function calls of the contract. The application has been tested by creating a wallet, which provides a medium to interact with the contract and perform the necessary functions.
9. Conclusion
This solution provides with a proper and unique strategy to encourage more people into the system to pool in money as the collateral, while providing them meaningful profits from the system and also stabilizing the system to maintain the stable value to a fiat currency. This not only helps in creating a stable ecosystem or currency structure but also increases economic activity and currency flow [6].
Additionally, the platform also ensures total functionality in all the discovered scenarios with proper integrity and completeness throughout all the components in this proposed system. The proposed system can be hence, easily integrated to an existing stablecoins structure or be created afresh.
10. References
Kenji Saito, Mitsuru Iwamura, “How to Make a Digital Currency on a
Blockchain Stable Future Generation Computer Systems, Volume 100,
2019, Pages 58-69.Klages-Mundt, Ariah & Minca, Andreea. (2019). (In) Stability for the
Blockchain: Deleveraging Spirals and Stablecoin Attacks.Ingolf G.A. Pernice, Sebastian Henningsen, Roman Proskalovich,
Martin Florian, Hermann Elendner, Björn Scheuermann, Monetary
Stabilization in Cryptocurrencies - Design Approaches and Open
Questions, IEEE Crypto Valley Conference on Blockchain Technology
(CVCBT), 28^th^ May 2019Black, Matthew & Liu, TingWei & Cai, Tony. (2019). Atomic Loans:
Cryptocurrency Debt Instruments, 16 Jan 2019.Stjepan Begušić, Zvonko Kostanjčar, Momentum and liquidity in
cryptocurrencies, 1 Apr 2019Peter Krafft, Nicolás Della Penna, Alex 'Sandy' Pentland, An
Experimental Study of Cryptocurrency Market Dynamics, CHI '18 2018